

The result is always rotated 90-degrees in a counter-clockwise direction for a 2D coordinate system where.

We assume that you are familiar with the standard $(x,y)$ Cartesian coordinate system in the plane.Įach point $\vc$. Returns the 2D vector perpendicular to this 2D vector. The green arrow always has length one, but its direction is the direction of the vector a. The length of the red bar is the magnitude a of the vector a. Here we will discuss the standard Cartesian coordinate systems in the plane and in three-dimensional space. The two defining properties of a vector, magnitude and direction, are illustrated by a red bar and a green arrow, respectively. When we express a vector in a coordinate system, we identify a vector with a list of numbers, called coordinates or components, that specify the geometry of the vector in terms of the coordinate system. Often a coordinate system is helpful because it can be easier to manipulate the coordinates of a vector rather than manipulating its magnitude and direction directly. We also discussed the properties of these operation. o is the lines orientation, a normalized direction vector (unit vector) pointing perpendicular to its run direction. An example of a predicate form of the vector line equation in 2D is: p o L Here, the line is represented by two features: o and L.
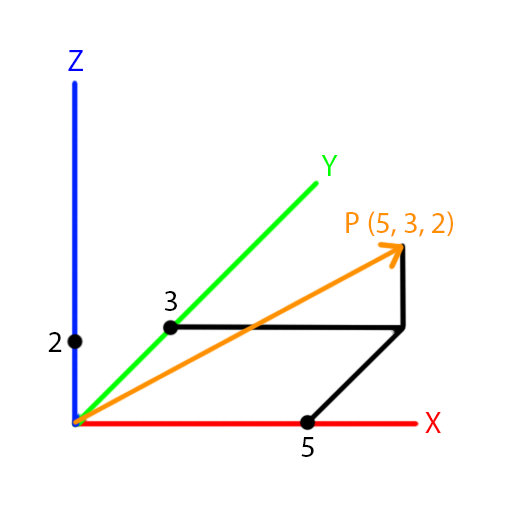
Of vectors, we were able to define operations such as addition, subtraction, In mathematics, a direction vector that describes a line D is any vector. In the introduction to vectors, we discussed vectors without reference to any coordinate system.īy working with just the geometric definition of the magnitude and direction


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
